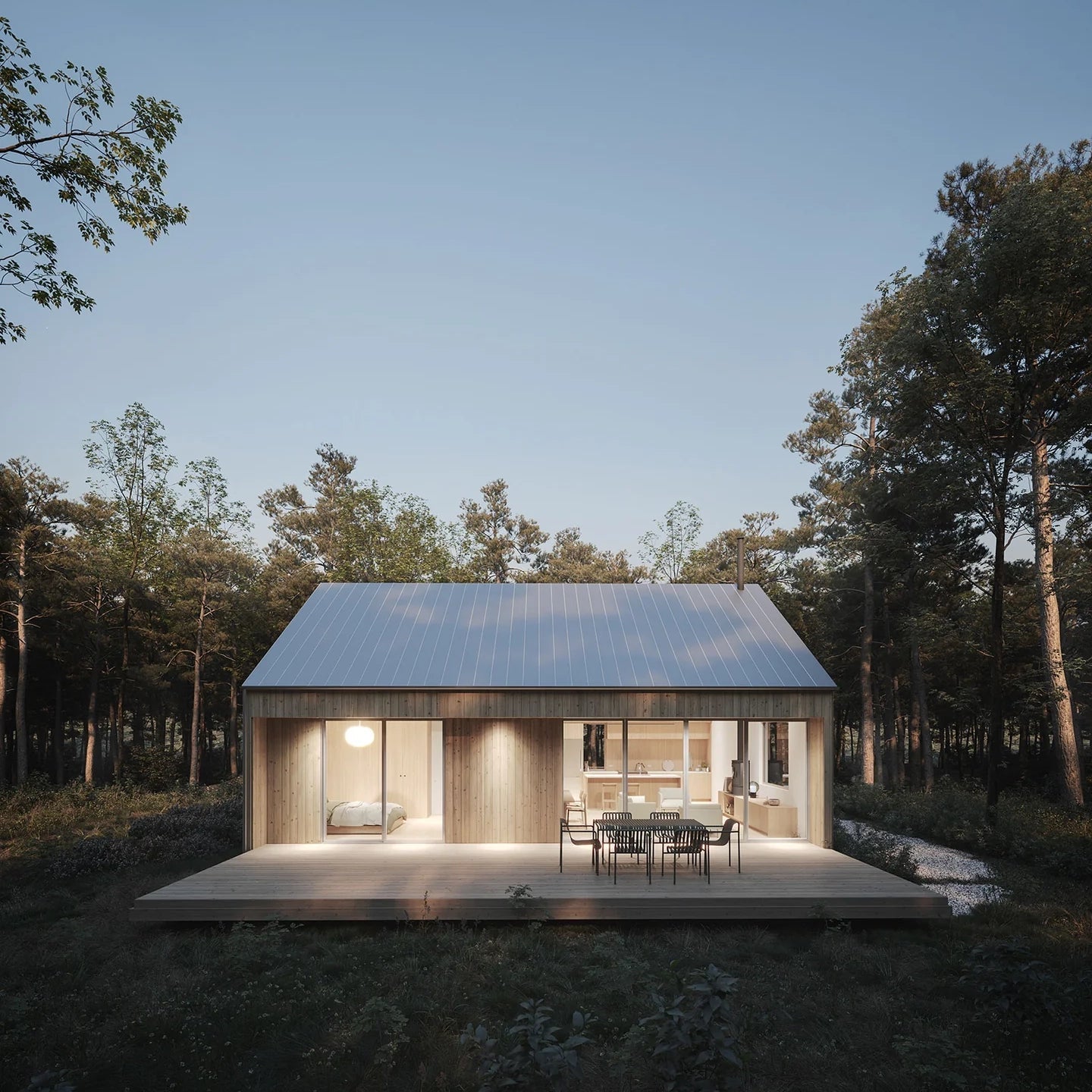
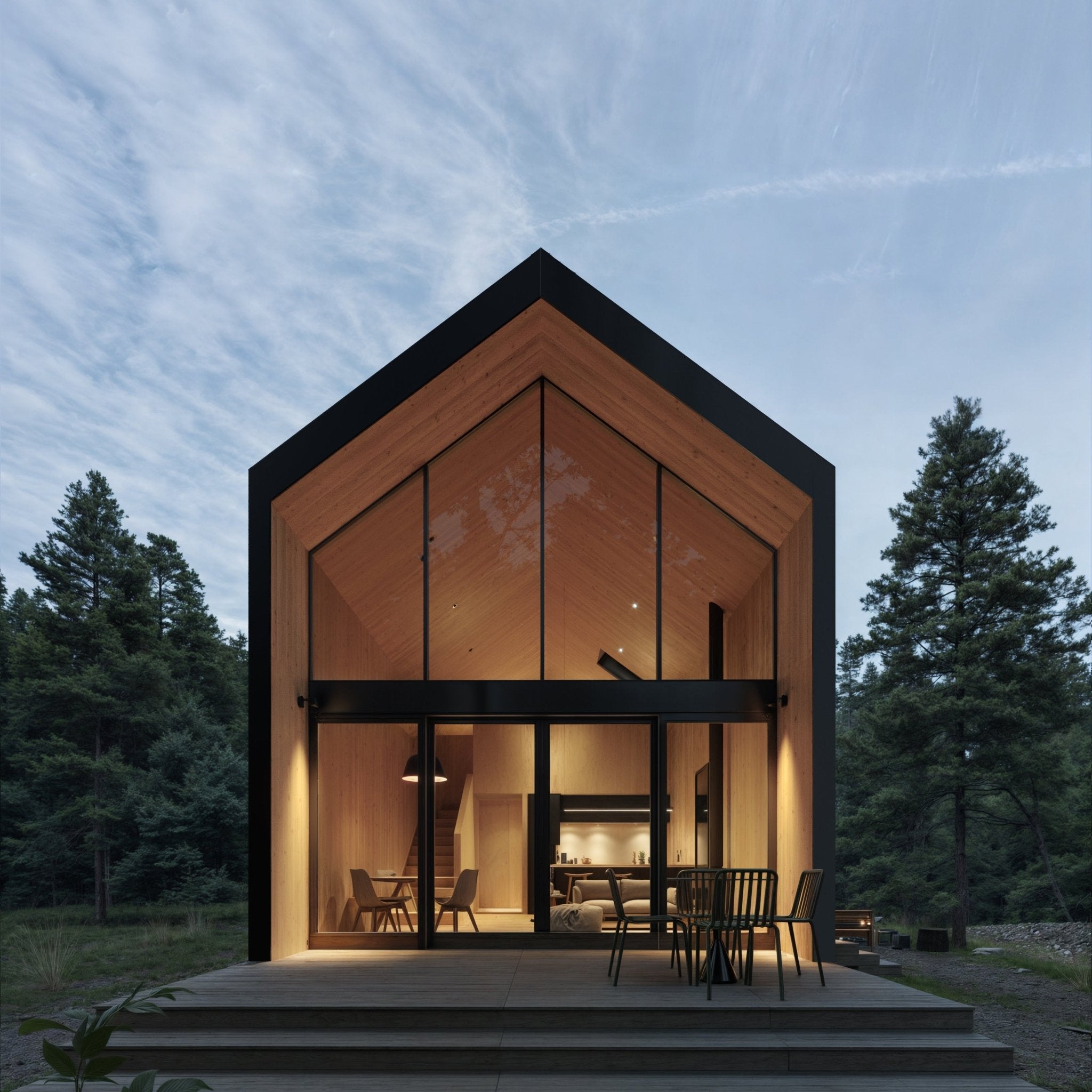
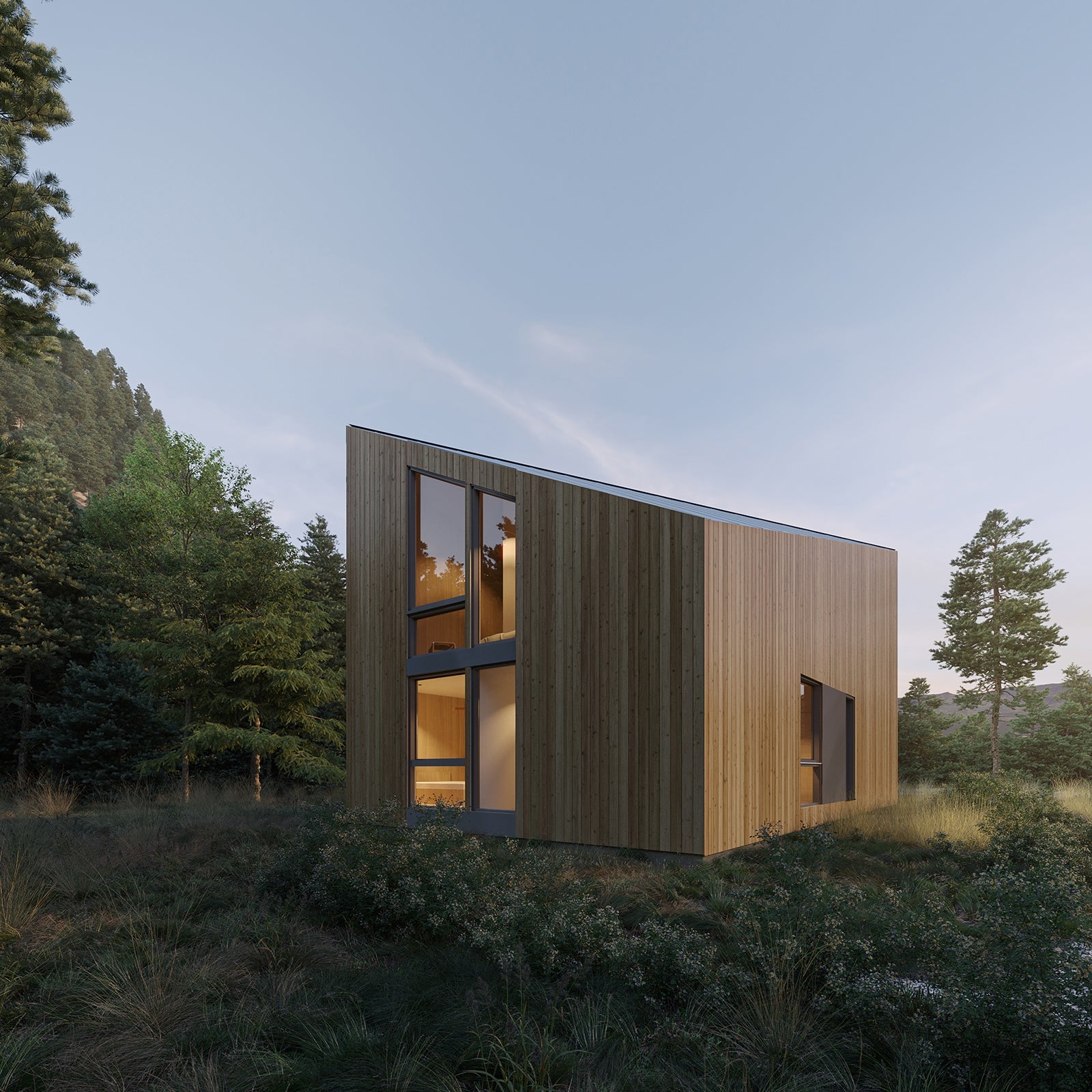
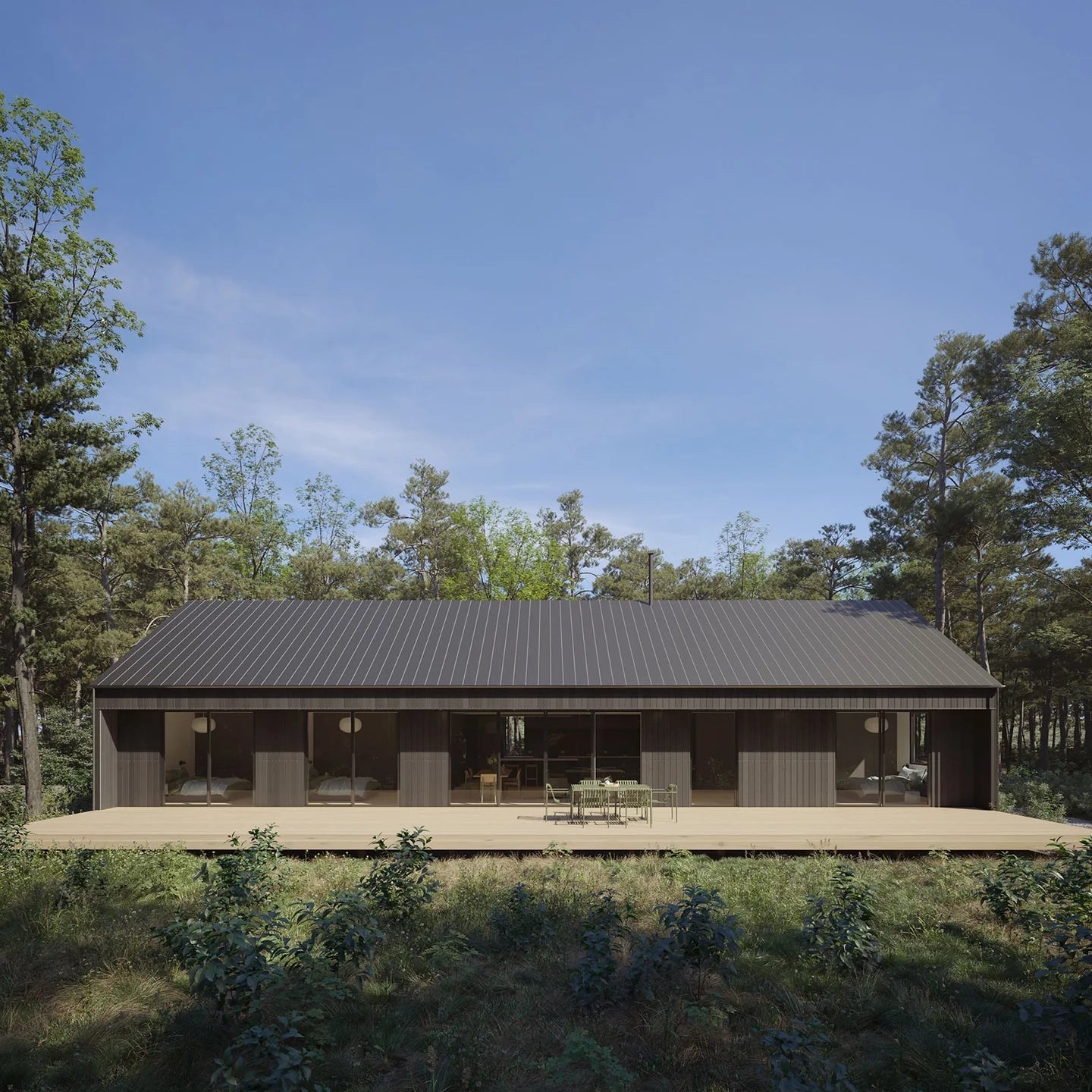
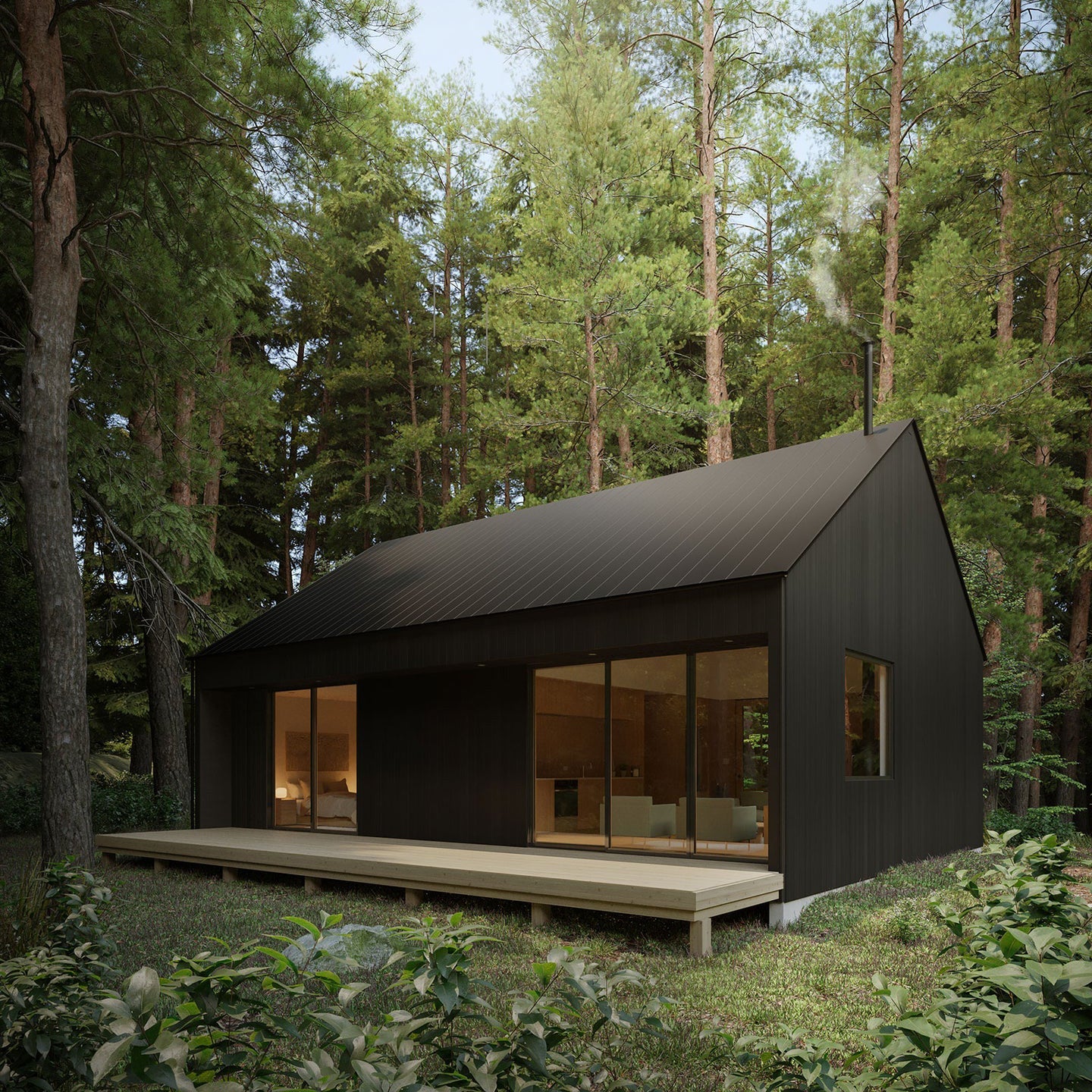
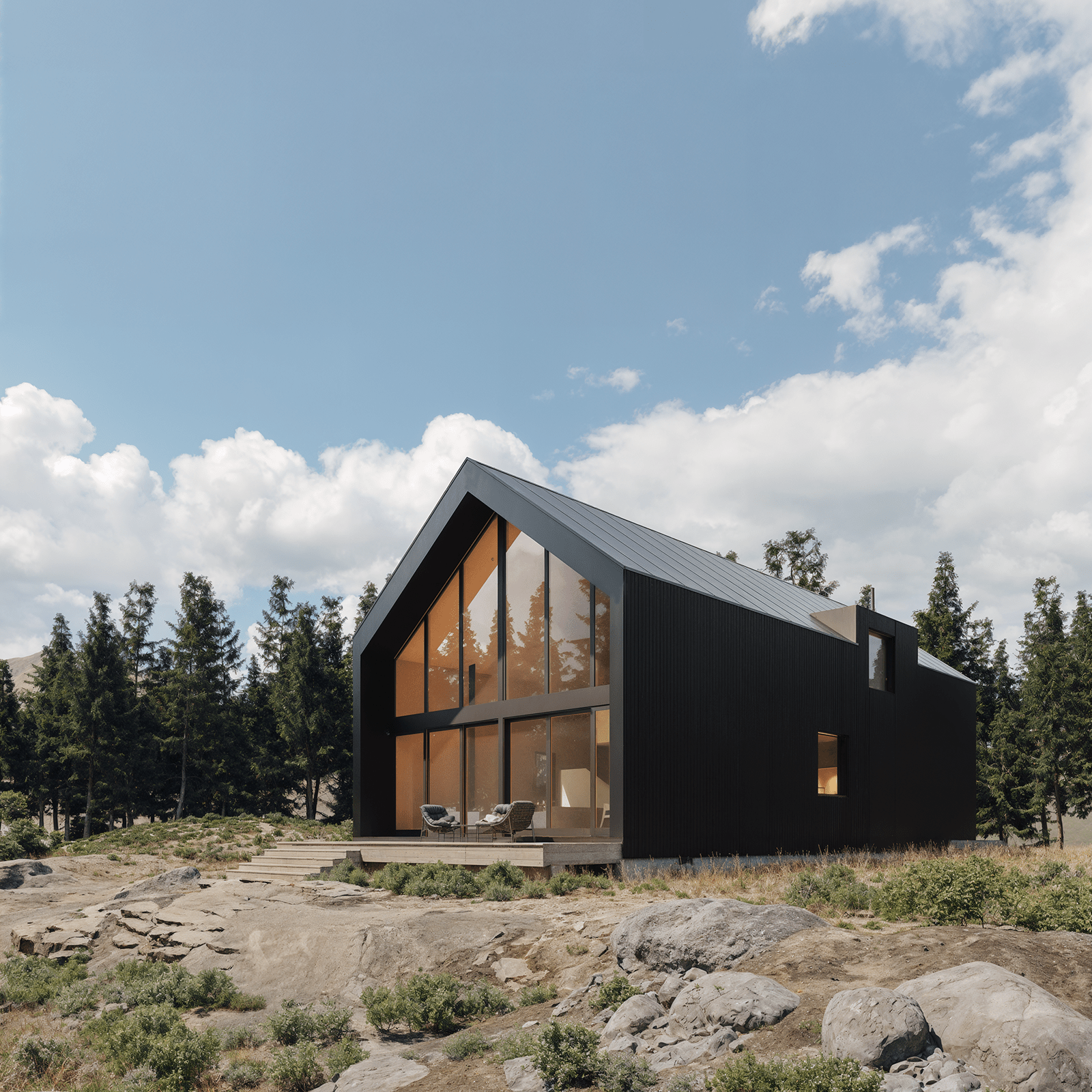
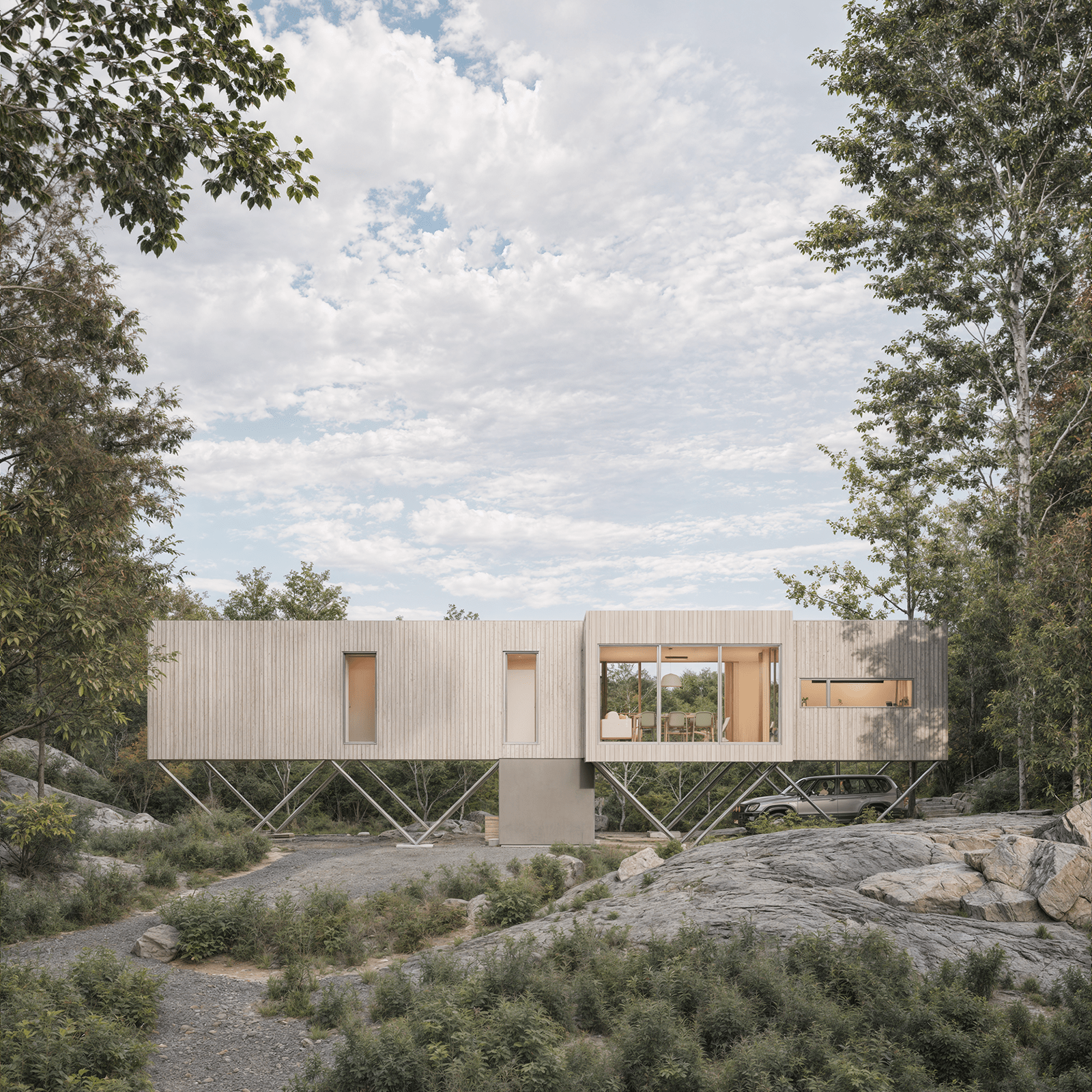
Prefab homes in Wisconsin
Prefab homes in Wisconsin built for four-season living—from rural countryside and lakefront properties to modern builds near Milwaukee, Madison, and Green Bay. Delivered as panelized kits with stamped plans.
Browse building kits
How much will it cost to build a prefab in Wisconsin?
Many owners budget about $160–$240 per sq ft for prefab construction in Wisconsin (home-only), with totals varying by finishes, site work, and location. Rural areas may require added expenses for Private Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems (POWTS/septic), well drilling, extensive site preparation, foundation considerations for Wisconsin's frost depth requirements, and utility line extensions to remote properties.
Wisconsin Prefab Resources
Custom Liquid
Zoning & Permits
Wisconsin enforces the Uniform Dwelling Code (UDC) statewide for one- and two-family dwellings, in effect since June 1, 1980. The Wisconsin Department of Safety and Professional Services administers the UDC, which is based on the International Residential Code but includes Wisconsin-specific amendments. The UDC is mandatory in all Wisconsin municipalities and cannot be modified to be more or less stringent locally. Contact your local building inspector or municipal office for permitting. The UDC covers manufactured, modular, and panelized homes.
Off-Grid & Rural Builds
For rural builds not connected to public sewer, Private Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems (POWTS) are regulated under Wisconsin Administrative Code SPS 383. The DSPS POWTS Program administers statewide standards. Sanitary permits are required and issued by county sanitation offices. Soil and site evaluation by a certified soil tester is mandatory before permitting. Systems must be designed by licensed professionals and inspected by state-certified POWTS inspectors. Contact your county zoning or environmental health office for permitting requirements.
Energy Code & Efficiency
Wisconsin has adopted the 2009 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) as part of the Uniform Dwelling Code, effective January 1, 2016. The energy code is mandatory statewide for residential construction. Compliance can be demonstrated using the federal REScheck program. The DSPS Uniform Dwelling Code page provides energy code resources. For commercial buildings, Wisconsin adopted the 2015 IECC. Contact your local building inspector for specific energy code compliance requirements.
Local Zoning Tools
Zoning in Wisconsin is administered at the municipal and county level. While the Uniform Dwelling Code is enforced statewide, local jurisdictions maintain authority over zoning regulations including setback requirements, lot coverage, and land use restrictions. The UpCodes Wisconsin resource provides code information by jurisdiction. Contact your local zoning office or county planning department for dimensional requirements and permitted uses. Counties also administer POWTS sanitary permits through their environmental health departments.
Tip
If you're unsure about your parcel's status—whether it requires POWTS approval through your county sanitation office, falls under specific local zoning restrictions, or needs special foundation considerations for Wisconsin's frost depth requirements—contact your local building inspector, county zoning office, or environmental health department directly. In Wisconsin, the Uniform Dwelling Code is mandatory statewide, but local zoning varies by jurisdiction. The resources above are a great place to start.